What Are Cryptocurrencies Used For?
What Are Cryptocurrencies Used For?
Published in August 2025 | Category: Crypto
Exploring Real-World Applications and Emerging Use Cases
Cryptocurrencies, once considered a niche interest of tech enthusiasts, have evolved into powerful financial instruments with wide-ranging applications. While their primary appeal has traditionally been speculation and trading, the true value of cryptocurrencies lies in their functionality and potential to transform global systems. In this article, we’ll explore the most relevant and practical uses of cryptocurrencies across different sectors and societies.
Table of Contents
- 1. Peer-to-Peer Transactions and Borderless Payments
- 2. Store of Value and Hedge Against Inflation
- 3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- 4. Stablecoins for Daily Transactions
- 5. NFTs and Digital Ownership
- 6. Crowdfunding and Tokenization
- 7. Micropayments and Content Monetization
- 8. Privacy and Financial Sovereignty
- 9. Governance and DAOs
- 10. Humanitarian Aid and Social Impact
- Conclusion: A Growing Ecosystem of Use Cases
1. Peer-to-Peer Transactions and Borderless Payments
One of the original and most fundamental use cases of cryptocurrencies is to serve as a decentralized medium of exchange. Bitcoin, the pioneer cryptocurrency, was created to facilitate peer-to-peer digital transactions without intermediaries such as banks or governments.

- Borderless payments: Cryptocurrencies allow for instant, low-cost cross-border transfers. This is especially beneficial for individuals in developing countries or underbanked populations who face high remittance fees.
- Reduced friction: International wire transfers can take several days and require heavy documentation. Crypto transactions can be completed within minutes without traditional gatekeepers.
Real-world example: Filipino overseas workers often use crypto services like Coins.ph and Binance Pay to send remittances home, saving up to 80% on fees.
2. Store of Value and Hedge Against Inflation
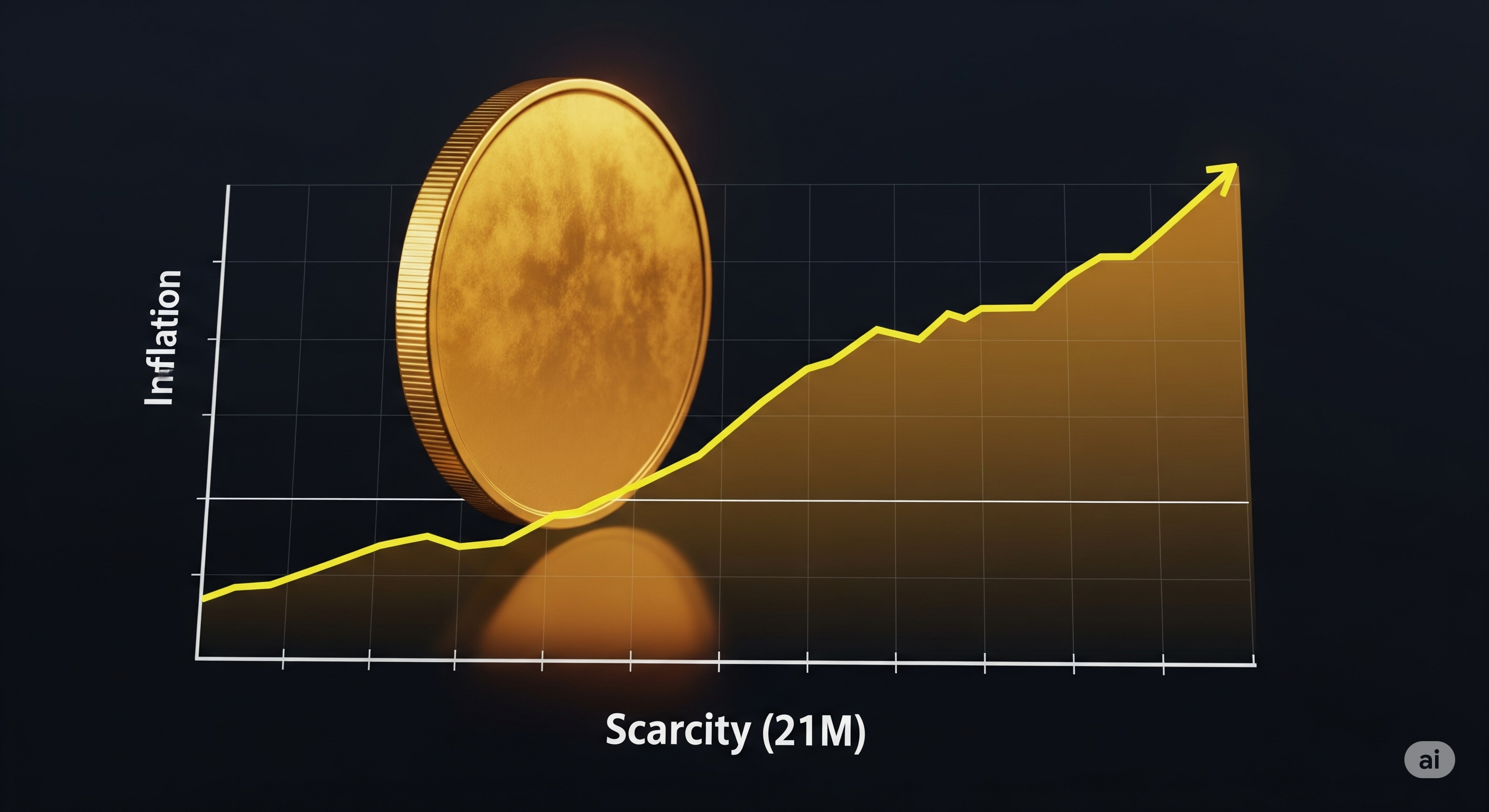
In regions suffering from high inflation or political instability, cryptocurrencies—especially Bitcoin—are increasingly used as a store of value.
- Digital gold: Bitcoin is often referred to as “digital gold” due to its limited supply (21 million coins). This scarcity makes it attractive as a hedge against inflation.
- Escape from fiat collapse: In countries like Venezuela, Zimbabwe, and Argentina, local currencies have lost much of their purchasing power. Citizens are turning to cryptocurrencies to preserve wealth.
Real-world example: In Venezuela, Bitcoin and stablecoins such as USDT are commonly used to transact in a hyperinflated economy where the bolívar is practically unusable for daily trade.
3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi refers to a new financial system built on blockchain technology, where users interact directly through smart contracts without intermediaries. It replicates traditional financial services like loans, savings, and trading.
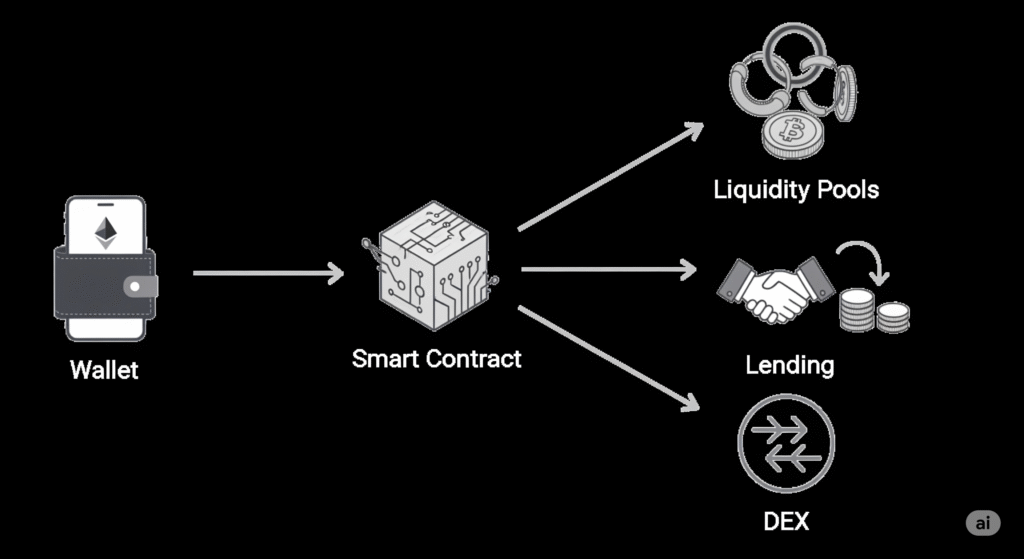
- Lending and borrowing: Platforms like Aave or Compound allow users to lend crypto and earn interest, or borrow assets by providing collateral.
- Yield farming: Investors can earn rewards by providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges like Uniswap.
- Synthetic assets: DeFi also enables the creation of tokens that represent real-world assets like stocks or commodities.
Benefits:
- No credit checks or banking restrictions.
- Transparent and programmable rules.
- Open to anyone with internet access.
4. Stablecoins for Daily Transactions
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets like the U.S. dollar or euro. Examples include USDT (Tether), USDC, and DAI.
Use cases:
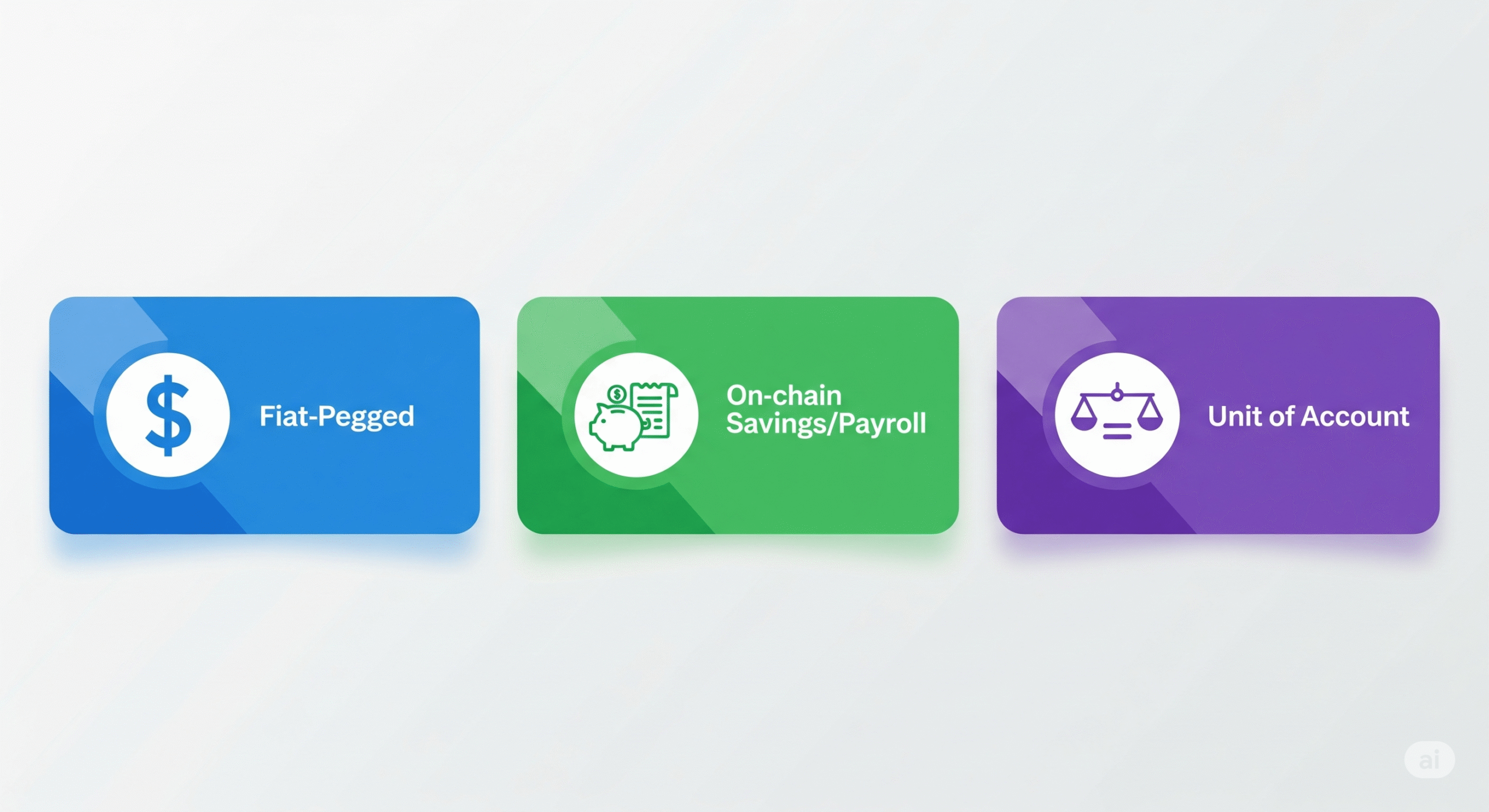
- Daily transactions: In economies with volatile currencies, stablecoins provide a stable unit of account.
- Payroll: Freelancers and remote workers are increasingly being paid in stablecoins.
- Savings: Stablecoins offer protection from local currency depreciation without needing access to foreign bank accounts.
Real-world application: Platforms like Bitwage allow workers in Latin America and Africa to receive part of their salaries in USDC.
This content may interest you!
5. NFTs and Digital Ownership
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) represent unique digital assets on the blockchain. While they initially gained attention through digital art and collectibles, their real potential goes beyond speculation.
Use cases include:
- Intellectual property and royalties: Artists and creators can receive automatic royalties when their work is resold.
- Identity and credentials: NFTs can be used to represent certificates, licenses, and access rights.
- Gaming: In blockchain games like Axie Infinity or The Sandbox, players can own and trade in-game assets as NFTs.

6. Crowdfunding and Tokenization
Cryptocurrencies have revolutionized fundraising through mechanisms like Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), Security Token Offerings (STOs), and Initial DEX Offerings (IDOs).
Benefits:
- Projects can raise capital globally without intermediaries.
- Investors gain access to early-stage opportunities.
- Tokens can represent equity, profit-sharing, or access rights.
Additionally, blockchain allows for the tokenization of real-world assets, such as real estate or artwork, enabling fractional ownership and liquidity.
7. Micropayments and Content Monetization
Traditional payment systems often impose high fees on small transactions, making them inefficient for low-cost digital services. Cryptocurrencies solve this with:
- Low-fee micropayments: Ideal for tipping, pay-per-article access, or micro-subscriptions.
- Empowering creators: Platforms like Mirror.xyz or Audius allow content creators to monetize directly without centralized intermediaries taking a large cut.
8. Privacy and Financial Sovereignty
While many blockchains are public and transparent, some cryptocurrencies are designed for privacy. Monero (XMR) and Zcash (ZEC) allow users to shield their transaction data.
Use cases:
- Protection from censorship and financial surveillance.
- Safe transactions in oppressive regimes or for vulnerable populations.
Important note: While privacy coins have legitimate uses, they also pose challenges in terms of regulatory compliance and anti-money laundering.
9. Governance and DAOs
Cryptocurrencies also play a key role in decentralized governance structures. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) use crypto tokens for voting and decision-making.
Examples:
- MakerDAO governs the DAI stablecoin protocol through token-holder voting.
- Gitcoin DAO funds open-source software development through community consensus.
This model enables new forms of collective organization and decision-making outside traditional institutions.
10. Humanitarian Aid and Social Impact
Cryptocurrencies are being used by NGOs and humanitarian organizations to deliver aid directly and transparently.
Benefits:
- Reduced overhead and corruption.
- Real-time, trackable disbursements.
- Access in areas with broken financial infrastructure.

Real example: UNICEF and Save the Children have experimented with receiving donations and distributing funds using cryptocurrencies.
Conclusion: A Growing Ecosystem of Use Cases
The utility of cryptocurrencies extends far beyond investment and trading. From enabling financial access in marginalized communities to powering the next generation of digital infrastructure, crypto is a transformative force. As adoption grows, we can expect more use cases to emerge, especially in areas where traditional systems have failed or lagged.
Whether it’s sending money home to your family, funding your startup, or buying digital real estate in the metaverse, cryptocurrencies offer powerful tools that are reshaping the global economy—and we’re only just beginning to see what’s possible.
